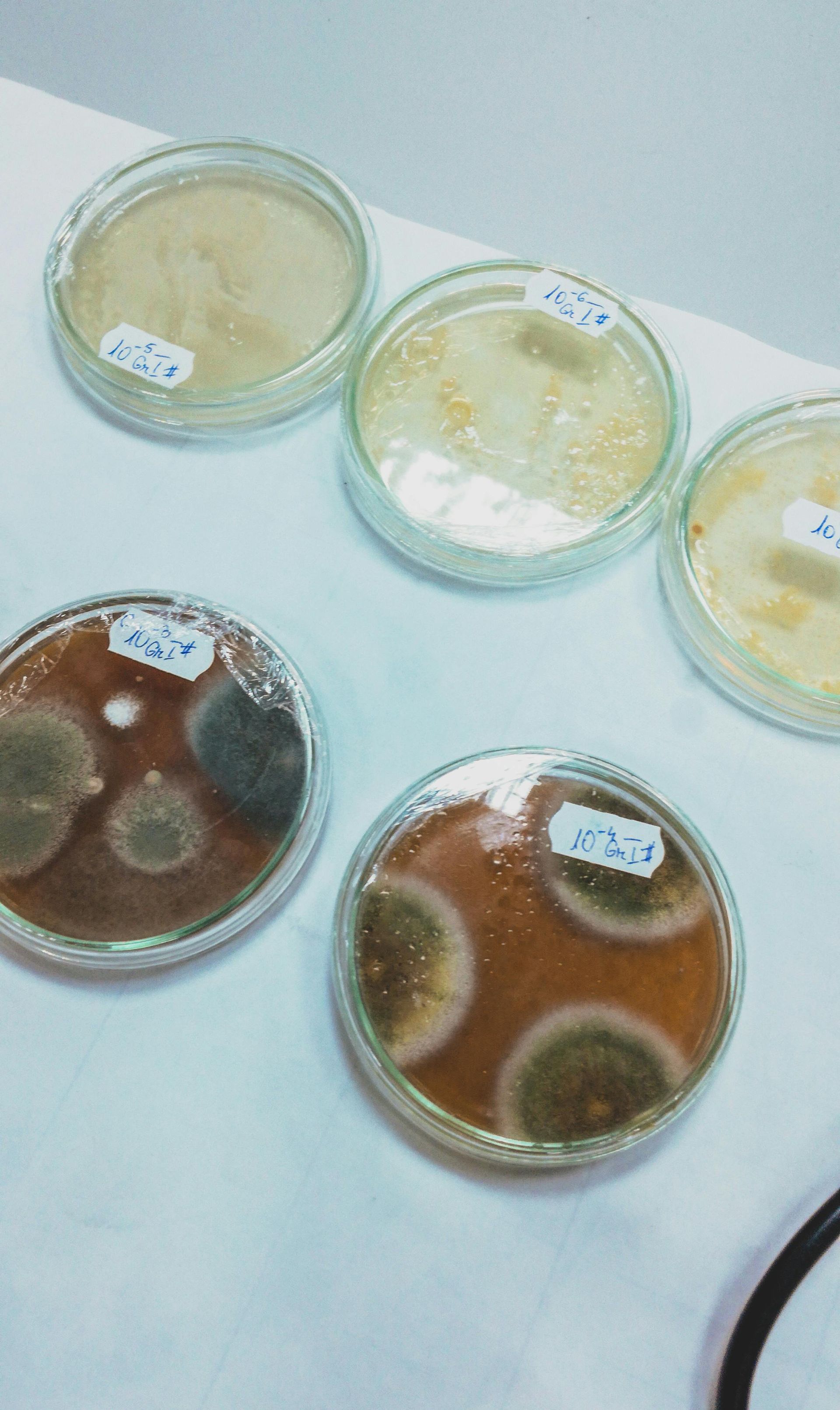
The Science and Evolutionary History of Mold
Mold is the original recycler. The main job of mold in nature is to assist in the break down decaying organic materials to return nutrients to the soil. The cellular structure of large, connected colonies of mold, called hyphae or hyphal networks, allow the sharing and transfer of water across the entire network. Thus, another evolutionary job that evolved for mold is the existence of mycorrhizal networks, which are symbiotic relationships that exist between mold colonies and the roots of certain types of trees.
The Inner Workings of Mold
The trees utilize the enlarged surface area and permeability of hyphal networks, and in exchange for access to carbohydrate resources provided by the roots of trees. – if there were a leaking pipe in the structure as we often see in our mold remediation work, the mold closest to the pipe would be able to transfer water, food and other nutrients to each other through the hyphal networks created by the complex mycorrhizal fungal networks linking fungi together. This ability originates in forests as a symbiotic relationships between certain types of trees and fungi, allowing the trees to collectively share water and other nutrients with each other through fungal growths connecting trees’ root networks within a certain proximity.
Understanding the existence of mycorrhizal networks is important in case you ever find yourself in a situation where wood or carpet in your home feels damp during times of exterior rain, even without any spills or leaks. The connected network of mold colonies means that water and nutrients can be shared across the entire collection of mold colonies, thus allowing you another way to detect the presence of mold in your home.
If you are concerned about mold growth, contact our mold remediation and mold testing company, headquartered in Massachusetts, to have a licensed and certified mold inspector perform mold testing services to give you the certainty you are looking for.